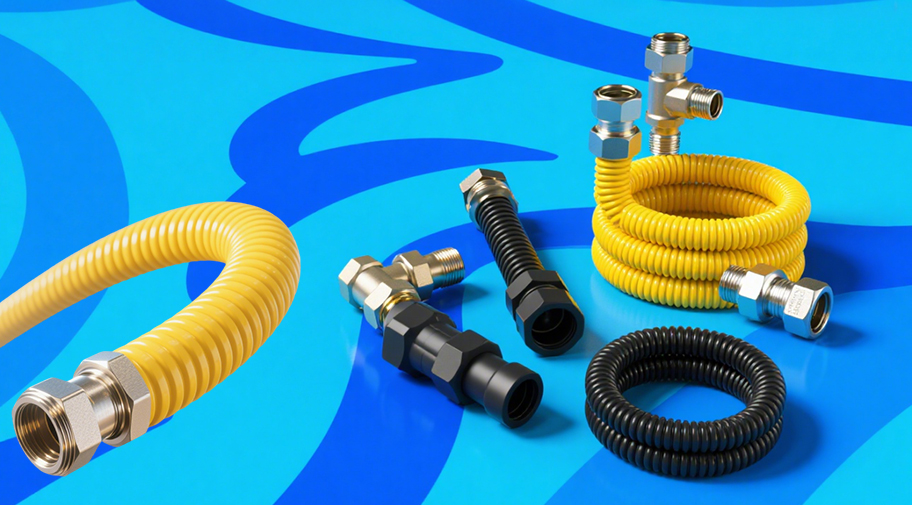
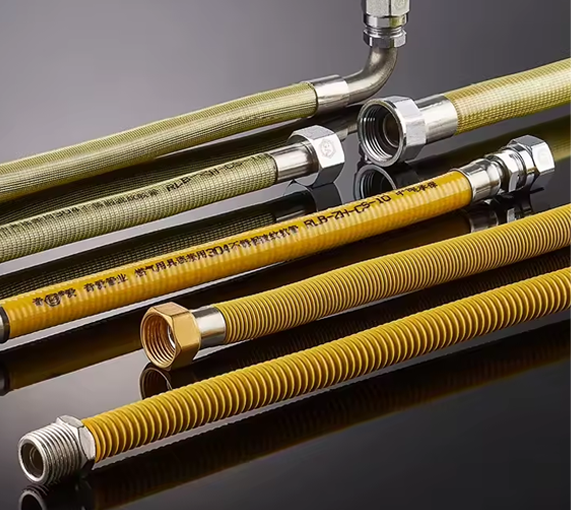
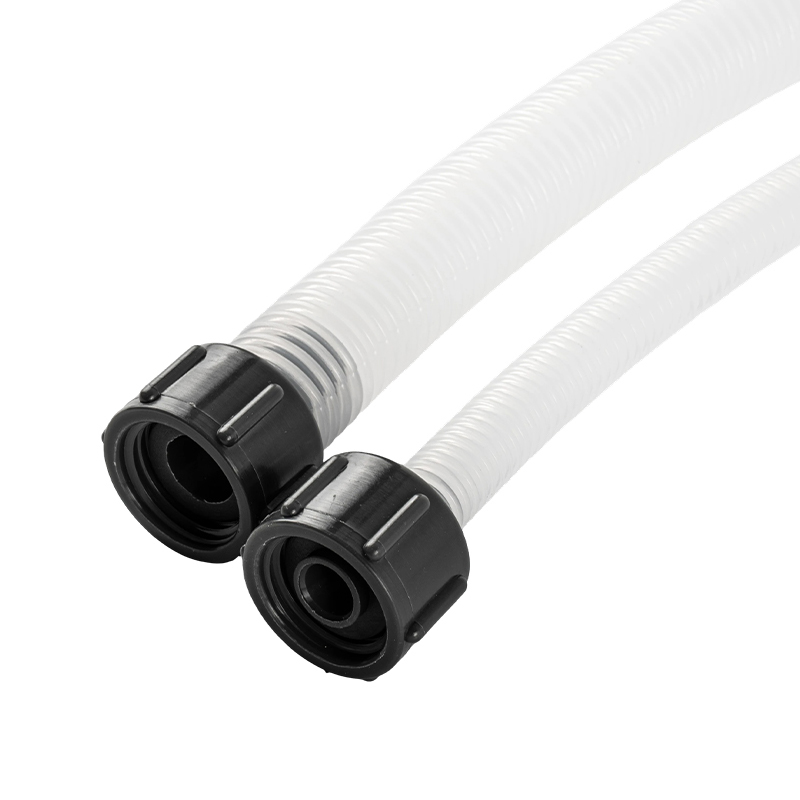
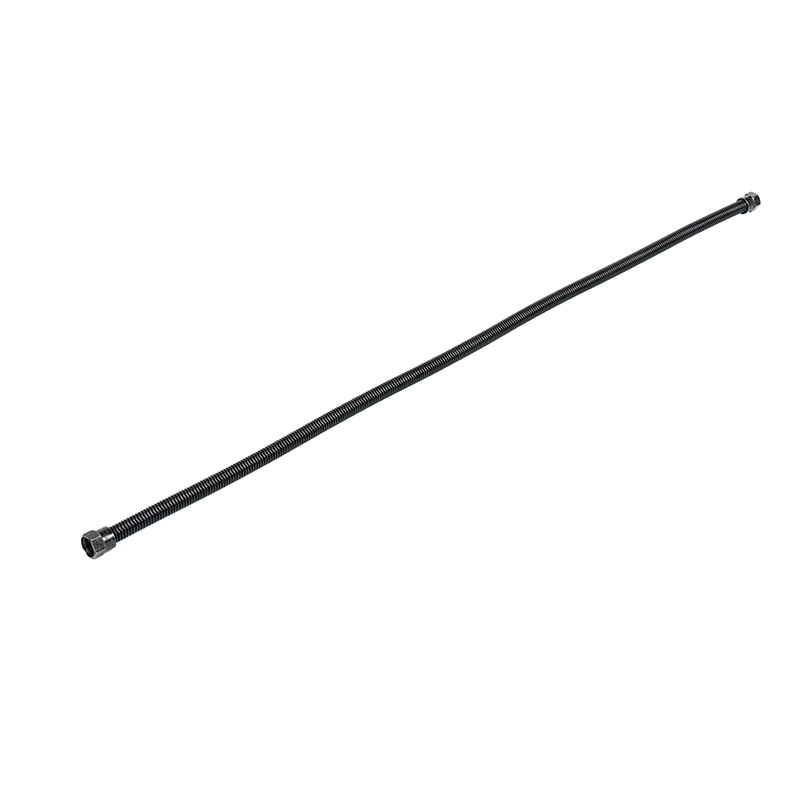
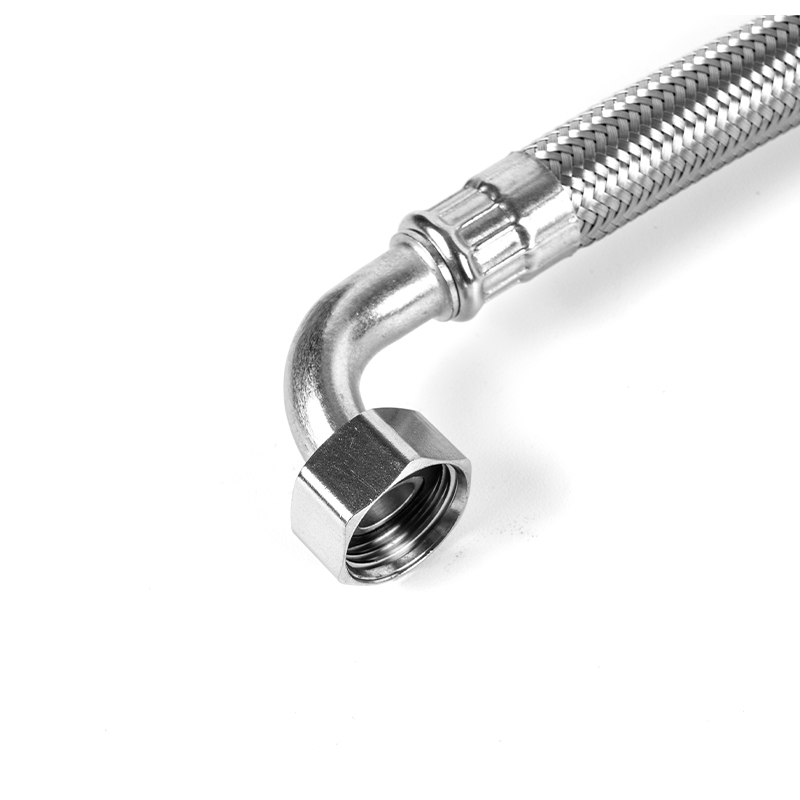
1. What is a PVC coated gas connector?
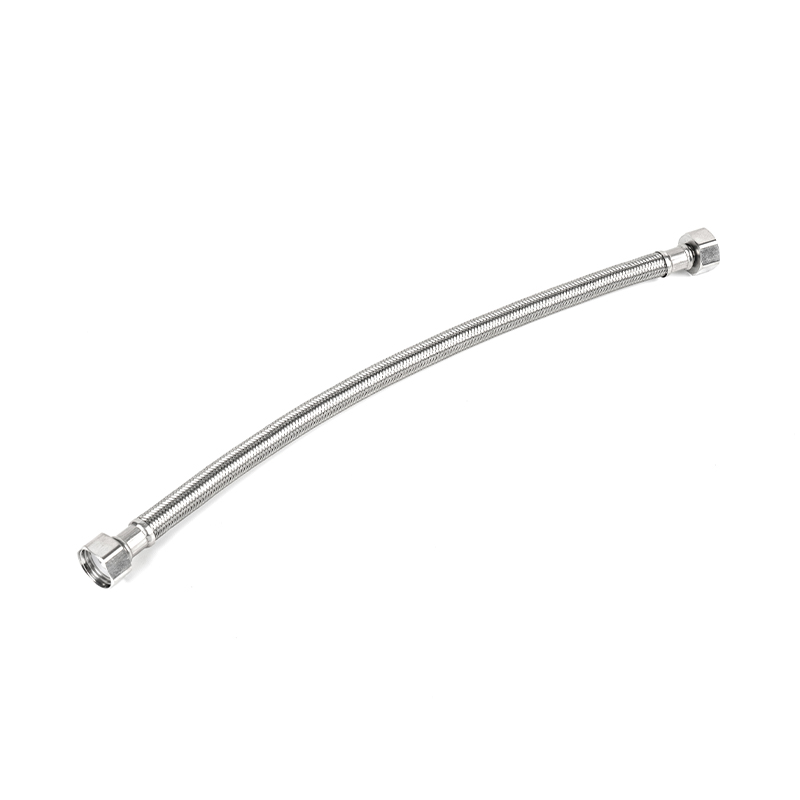
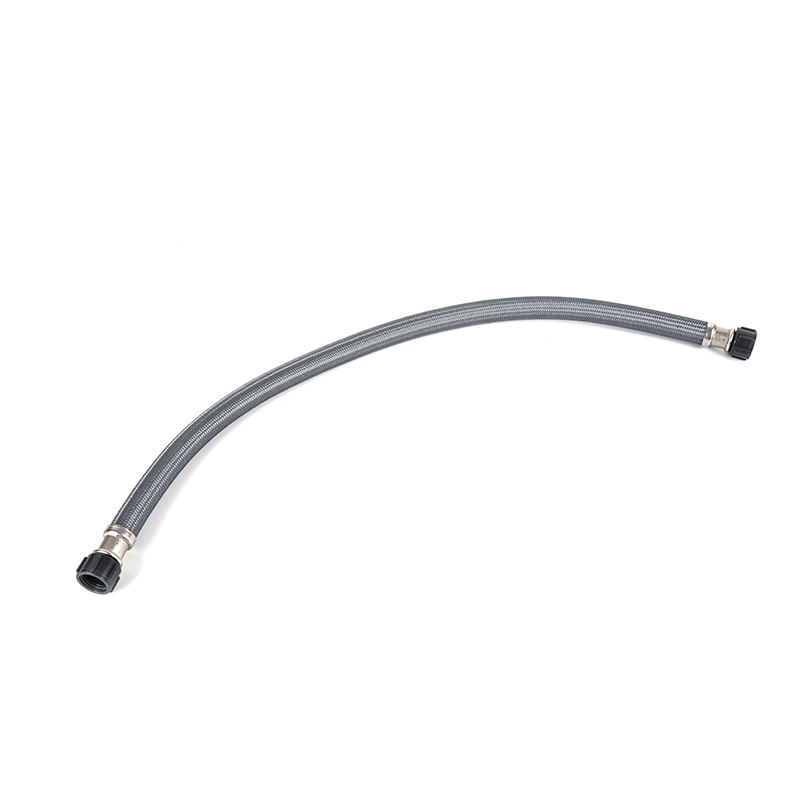
A PVC coated gas connector is a flexible connecting device widely used in household, commercial kitchen, and industrial gas systems. It is primarily used to connect gas pipelines to gas appliances such as gas stoves, water heaters, and heating furnaces. It consists of two parts: an inner metal corrugated pipe or metal hose, and an outer layer of high-strength PVC (polyvinyl chloride) protective coating. The inner metal layer is responsible for withstanding gas pressure, maintaining structural strength, and providing high-temperature resistance; the outer PVC coating provides additional corrosion resistance, wear resistance, oil resistance, and insulation protection, making it more suitable for the complex usage conditions in a household environment.
Compared with traditional rubber hoses, PVC coated gas connectors integrate the pressure resistance of metal hoses with the flexibility of PVC material. This combined structural design offers advantages such as safety, durability, and ease of maintenance. Especially in environments with heavy kitchen grease, significant temperature fluctuations, and frequent exposure to moisture, the outer PVC coating effectively prevents the metal hose from corroding due to grease and moisture, extending its overall service life.
The internal metal material of the PVC coated gas connector typically uses 304 stainless steel or galvanized steel, which possess excellent tensile strength, aging resistance, and high-temperature resistance. From a structural perspective, the inner corrugated pipe uses a corrugated design, maintaining flexibility while under pressure, allowing the hose to be easily bent and routed in confined spaces without affecting sealing or root strength.
The outer PVC coating usually uses food-grade or high-molecular-weight corrosion-resistant materials, with the following characteristics:
Oil resistance: Kitchen grease will not directly adhere to the metal.
Moisture resistance: Prevents metal oxidation caused by humid environments.
Wear resistance: Reduces the risk of the metal hose being scratched when in contact with walls or cabinet edges.
Insulation safety: Prevents exposed metal parts from causing static electricity or safety hazards. PVC-coated gas connectors also feature a variety of standardized interface types, such as internal threads, external threads, and quick-connect fittings, facilitating connection to gas appliance interfaces in various countries and regions. Their production must comply with multiple safety standards, such as the American CSA certification, the European CE certification, and relevant Chinese GB/T standards.
PVC-coated gas connectors are modern gas connectors that combine safety, high performance, and long service life, effectively improving the safety and convenience of gas use.

2. The Role of PVC-Coated Gas Connectors
PVC-coated gas connectors play an indispensable role in modern gas systems. Their main functions can be analyzed from four aspects: safety, functionality, durability, and convenience.
(1) Providing a Flexible Gas Connection Method
Traditional gas systems use rigid metal pipes to connect gas equipment. While they offer strong sealing, they lack flexibility, making it very inconvenient if the equipment needs to be moved or repositioned. The internal stainless steel corrugated structure of PVC-coated gas connectors provides excellent flexibility, allowing for easy adjustment of direction and angle as the equipment position changes, without requiring extensive modification of the gas pipeline. This flexible connection method improves installation convenience and reduces the risk of leaks caused by stress concentration.
(2) Enhancing the Safety of the Gas Pipeline System
PVC-coated gas connectors offer multiple safety protections:
Metal inner layer provides mechanical strength
The internal stainless steel can withstand high pressure, tension, and impact, effectively preventing rupture caused by accidental collisions.
Outer PVC layer provides isolation protection
It isolates the metal from factors that cause long-term corrosion, such as oil, moisture, and chemical corrosive substances.
Prevents external damage
The PVC coating acts as a buffer when the hose is close to cabinets, walls, or equipment casings.
Reduces static electricity and contact risks
The insulating layer prevents potential electric shock or static sparks caused by exposed metal.
This multi-layered structure makes these connectors more suitable for high-humidity and high-oil environments such as kitchens. Compared to exposed metal hoses or rubber hoses, the safety factor is significantly improved.
(3) Extending Service Life
The PVC coating significantly reduces external environmental corrosion of the internal metal, greatly extending the overall lifespan of the product. The outer layer material is wear-resistant, oil-resistant, and chemically resistant, combined with the pressure-resistant internal stainless steel structure, giving it a typical lifespan of 5–15 years. This makes it ideal for long-term use in applications where frequent replacement is not feasible, such as built-in cooktops or commercial kitchen equipment.
(4) Improved Gas Usage Efficiency
The smooth, low-resistance internal structure of PVC-coated gas connectors allows for smoother and more stable gas flow, which is especially important for equipment requiring constant gas pressure (such as water heaters and industrial burners). Stable flow improves equipment combustion efficiency and reduces energy waste.
(5) Provides Better Installation Adaptability
Modern kitchens and equipment layouts are often complex, and traditional rigid pipes are difficult to adapt to space requirements. The flexibility and bendability of PVC-coated gas connectors make them suitable for various narrow or irregular spaces. Whether it's built-in stoves, central gas systems, or centralized connections for multiple gas appliances, installation is easily achieved.
The color of the PVC coating (commonly yellow) also serves as a warning, making the hose easier to identify and inspect, aiding in daily maintenance and safety checks.
PVC-coated gas connectors are not just simple connecting fittings, but an important component in the entire gas system, improving safety, increasing efficiency, and optimizing installation.
3. What to pay attention to when using PVC-coated gas connectors?
Although PVC-coated gas connectors offer high safety, to ensure long-term stable operation and reduce the risk of gas leaks, the following points should be noted during use:
(1) Regularly check the hose for aging
The PVC coating may show signs of aging after prolonged exposure to high temperatures, humidity, and oil fumes, such as stickiness, discoloration, cracking, and bulging. Regular checks (recommended every 6–12 months) can effectively identify potential risks.
(2) Do not excessively bend or stretch the hose
Although PVC-coated gas connectors have good flexibility, excessive bending (less than the specified bending radius) can lead to:
Internal metal fatigue
Deformation of the corrugated structure
Cracking of the PVC coating
The correct practice is to use natural curves and avoid right-angle bends.
(3) Avoid proximity to open flames or high temperatures
Although the PVC coating can withstand certain temperatures, prolonged exposure to high temperatures will accelerate aging and may even cause the hose to soften and deform. The hose should be kept away from stove casings or areas with open flames.
(4) Do not allow the hose to bear external weight
The hose should not bear the weight of gas appliances or cabinets, nor should it be suspended or stretched tightly. Otherwise, the internal metal structure may deform due to prolonged stress concentration, leading to loose connections or leaks.
(5) Avoid contact with sharp objects
Sharp objects can damage the PVC coating or puncture the internal metal structure, leading to leaks or bursts. During installation, ensure the route is smooth and away from metal corners or sharp edges.
(6) Do not reuse or reinstall
The hose connectors usually have a single-use sealing structure. The seal may be damaged after disassembly, so it is not recommended to reuse old hoses. The hose should be replaced every time the equipment is replaced.
(7) Pay attention to hose length selection
Insufficient hose length will cause it to be in a stretched state, affecting its lifespan; excessive length can easily cause kinking, dragging on the ground, and friction damage. It is generally recommended to choose a length slightly longer than the straight-line distance to ensure natural bending.
(8) Avoid unauthorized modification, welding, or extension
Any modification will destroy the structural integrity and pose serious safety hazards. The hose must remain in its factory condition and should not be cut or extended without authorization.
(9) Regular cleaning is required in high-grease environments
Grease can cause long-term corrosion of the PVC and metal layers. Therefore, commercial kitchens or home kitchens with heavy grease should regularly clean the surface with a damp cloth and keep it dry.
In general, proper use of PVC-coated gas connectors can greatly improve their lifespan and safety. If any abnormalities are found, such as unusual odors, loose connections, or hose deformation, immediately turn off the gas supply and contact a professional for assistance.

PVC-Coated Gas Connector Usage Guidelines:
| Category | Precautions | Reasons/Risks |
| Pre-Installation | Verify gas-specific certification (e.g., EN 14800, GB/T 26002) | Non-certified PVC may degrade under pressure or gas exposure, causing leaks. |
| Application | Low-pressure household use only (stoves, water heaters) | Limited pressure tolerance (≤0.1MPa); unsuitable for commercial/high-pressure systems. |
| Length | Max ≤1.5 meters; avoid excessive bending. | Long lengths may restrict flow or strain connections. |
| Bend Radius | Maintain ≥8cm natural curves; no sharp bends. | Kinks can damage internal metal layers. |
| Temperature | Ambient range: -10°C to 60°C; keep >30cm from flames. | PVC softens at high temps; becomes brittle in cold. |
| Fastening | Use stainless steel clamps (no plastic ties). | Metal clamps resist loosening; plastic degrades. |
| Physical Protection | Avoid contact with sharp edges; use protective sleeves in cabinets. | PVC coating scratches easily, exposing metal to corrosion. |
| Cleaning | Wipe with damp cloth; no solvents (alcohol/acetone). | Solvents dissolve PVC coating. |
| Lifespan | Replace every 3-5 years (even if undamaged). | Internal metal corrosion may be invisible. |
| Leak Response | If gas odor detected: 1. Shut valve 2. Ventilate 3. No electrical switches. | PVC damage can generate static sparks. |
Comparison with Metal Hoses:
| Feature | PVC-Coated Hose | Stainless Steel Hose |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (PVC barrier) | Good (depends on steel grade) |
| Pressure Rating | Low (≤0.1MPa) | High (≥0.4MPa) |
| Aesthetics | Custom colors available | Metallic finish only |
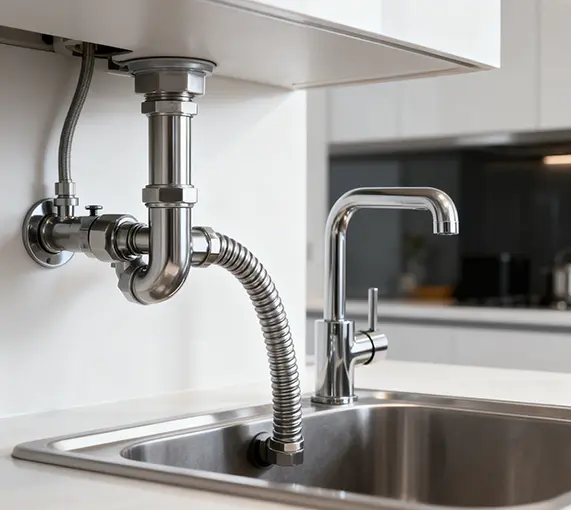
4. How to install a PVC coated gas connector?
The correct installation of a PVC coated gas connector directly affects the safety performance of the gas system. The following are detailed installation steps and precautions:
(1) Preparation before installation
Confirm the hose length and specifications: Select the matching connector size (such as G1/2, G3/4, etc.).
Check if the product is intact: Ensure there are no cracks, dents, or peeling.
Close the gas valve: Ensure safety during the installation process.
(2) Connecting to the gas valve end
Clean the threaded part of the gas valve end.
Align the connector of the PVC coated gas connector with the valve interface.
Manually screw in the threads and ensure proper alignment to avoid stripping the threads.
Use a wrench to tighten appropriately, but not excessively, to avoid damaging the sealing ring.
(3) Connecting to the gas appliance end
Connect the other end to the gas stove or gas water heater's inlet using the same method. Ensure a tight connection with no gaps.
(4) Safety check after installation
After installation, a leak test is required:
Apply soapy water to the connector.
Slowly open the gas valve.
Observe if any bubbles are produced.
If bubbles appear, it indicates a leak at the connection, and you should immediately retighten or reinstall.
(5) Routing and fixing
Check that the hose is not excessively bent.
Ensure the hose does not come into contact with power lines, sharp objects, or high-temperature areas.
If necessary, use clips or brackets to support the hose, allowing it to be in a naturally curved state.
(6) Final confirmation and activation
After confirming there are no leaks, close the valve and clean any moisture near the connector. Activate the gas appliance for testing, observing whether the combustion is normal and the flame is stable.
Correct installation not only improves gas safety but also extends the life of the hose and reduces frequent maintenance costs.
PVC-Coated Gas Connector Installation Guidelines:
| Step | Procedure | Tools/Materials | Key Precautions | Inspection Criteria |
| 1. Shut Off Gas | Turn off main gas valve | Wrench | Verify complete shutoff; ventilate area | Valve handle perpendicular to pipe |
| 2. Remove Old Hose | Detach existing connector | Adjustable wrench | Check pipe threads for damage | No cracks/deformation on threads |
| 3. Select Correct Hose | Confirm: - Length ≤1.5m - EN 14800/GB 26002 certified | Measuring tape | Never use non-gas-rated PVC hoses | Clear "GAS" marking on sleeve |
| 4. Install Clamps | Secure with stainless steel clamps at both ends | Clamp tool, 304SS clamps | Plastic zip ties prohibited | Tug test confirms no slippage |
| 5. Connect Appliances | Attach to appliance first, then gas line | PTFE tape (for threaded joints) | Avoid over-tightening (hand-tight + ¼ turn) | Natural bend; no forced alignment |
| 6. Leak Test | Apply soap solution to all joints | Soapy water, brush | No open flames during test | Zero bubbles for 3+ minutes |
| 7. Secure Routing | Fasten with clips every 50cm; maintain ≥8cm bend radius | Mounting clips | Keep >30cm from heat sources | No contact with sharp edges |
| 8. Final Check | Slowly open valve; sniff for gas odor | Gas detector (recommended) | If leak detected, shut valve immediately | No gas odor detected |
Why Choose PVC-Coated?
| Scenario | Recommended? | Reason |
| Household stove (natural gas) | Yes | Aesthetic, corrosion-resistant |
| Commercial kitchen | No | Insufficient pressure rating |
| Outdoor BBQ | No | Vulnerable to UV/weathering |
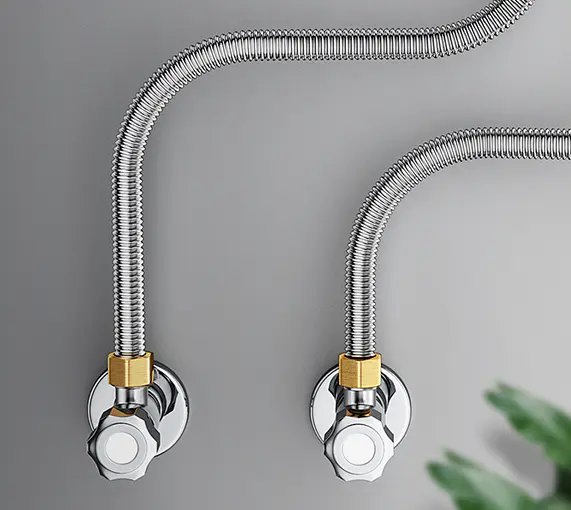
5. How to Maintain PVC Coated Gas Connectors
PVC coated gas connectors are widely used in home kitchens, commercial kitchens, and various gas appliances due to their flexibility, safety, and corrosion resistance. Although they are inherently strong and durable, lack of proper maintenance can still lead to safety hazards such as aging, leakage, and damage. To ensure safe gas use and extend product life, daily maintenance is crucial.

(1) Key Maintenance Points During Daily Use
Although PVC coated gas connectors have good flexibility and durability, they may still be affected by factors such as temperature, oil stains, pulling, and corrosion during long-term use. Therefore, the following maintenance details should be noted during daily use:
1) Regularly Check the Appearance
Check the outside of the hose at least every 3-6 months for:
Cracks, yellowing, or hardening
Bulging, peeling, or loosening of the surface
Signs of crushing or external force
Loose or rusty connectors
If any abnormalities are found, the hose should be replaced immediately to avoid the risk of gas leakage.
2) Avoid the Hose Being in a Stretched or Twisted State for Extended Periods
Although PVC coated gas connectors are flexible, they should not be:
Pulled too tightly
Bent at too sharp an angle (avoid right-angle bends)
Squeezed in gaps between cabinets or equipment
Bearing the weight of equipment
The correct practice is to maintain a natural curve, ensuring that the hose can stretch freely and is not under tension. This prevents internal metal fatigue, cracking of the PVC coating, or loosening of the connectors.
3) Avoid Contact with Open Flames and High-Temperature Areas
PVC coatings have a certain temperature resistance, but prolonged contact with flames or high-temperature surfaces can lead to:
Softening and deformation of the outer PVC layer
Accelerated aging of the internal metal due to heat
Reduced sealing performance
When using, ensure that the hose maintains sufficient distance from the stove flame, and install a heat shield if necessary.
4) Avoid contact with grease, chemical cleaning agents, and sharp objects
Kitchen grease accelerates the aging of PVC, while acidic or solvent-based cleaning agents may corrode the outer coating; sharp objects can directly damage the outer protection, exposing the metal layer. Therefore, avoid:
Using strong acids or strong solvents to clean the hose
Allowing knives or metal edges to scratch the hose
Soaking the hose in sewage or grease for extended periods
If cleaning is necessary, simply wipe with clean water or a neutral detergent.
5) Regularly check for leaks
Every month, or after moving the gas stove or water heater, a simple leak check should be performed:
Apply soapy water to the joints
Open the gas valve
Check for continuous bubbles
If bubbles appear, immediately close the valve and reinstall or replace the hose.
(2) Key points for long-term maintenance and upkeep (extending service life)
In addition to daily maintenance, long-term maintenance is also crucial. The following methods can effectively extend the service life of PVC-coated gas connectors and improve the overall safety of the gas system.
1) Replace regularly, do not exceed the service life
Although PVC-coated gas connectors typically last 5–10 years, their lifespan is affected by environmental differences, such as kitchens with heavy grease, which accelerate aging. Therefore, it is recommended:
Household kitchens: Replace every 3–5 years
Commercial kitchens: Replace every 1–3 years
If signs of aging are found, replace immediately and do not continue to use
Using expired hoses significantly increases the risk of leaks.
2) Avoid frequent disassembly and reinstallation
Many gas connector joints use a one-time sealing structure, and repeated disassembly may lead to:
Seal ring displacement
Thread wear
Reduced sealing performance
Therefore, when replacing gas appliances or rewiring, prioritize using new hoses and avoid reusing old ones.
3) Keep the installation environment dry and well-ventilated
Moisture accelerates PVC aging, and grease and oil fumes can adhere to the coating surface and cause long-term corrosion. Therefore, you should:
Regularly clean the area around the hose
Avoid water vapor remaining on the hose surface for extended periods
Maintain good ventilation in the kitchen to reduce grease and oil fume accumulation
A good environment can significantly extend the life of the hose.
4) Avoid crushing, impact, or external pressure.
When decorating, moving furniture, or organizing cabinets, avoid:
Placing heavy objects on the hose
Hitting the hose with tools
Squeezing the hose into narrow gaps
External force can deform the internal corrugations of the metal, leading to a risk of leakage.
5) Pay special attention to the connector area.
More than 70% of gas leaks originate from the connectors, not the hose itself. Therefore, special attention should be paid to:
Whether the connector is loose
Whether the sealing ring is cracked
Whether there is rust or oil buildup at the connector
If any abnormalities are found, the hose should be immediately reinstalled or replaced.
Maintaining PVC-coated gas connectors is not complicated, but each maintenance measure directly relates to gas safety in home and commercial environments. Through proper use, regular inspection, and reasonable maintenance, you can effectively extend the life of the hose, prevent gas leaks, and ensure the long-term safety of your living and working environment.
Maintenance Checklist for PVC Coated Gas Connectors:
| Maintenance Task | Procedure | Frequency | Tools/Materials | Key Precautions |
| Visual Inspection | Check for cracks, peeling, or abrasions on PVC coating. | Monthly | Visual check | Replace immediately if inner metal layer is exposed. |
| Leak Test | Apply soapy water to joints; observe for bubbles. | Every 6 months | Soap solution, brush | Never use open flames. Tighten fittings if leaks detected. |
| Clamp Check | Inspect stainless steel clamps for rust/looseness. | Annually | Wrench | Replace corroded clamps; plastic ties are prohibited. |
| Surface Cleaning | Wipe PVC surface with damp cloth (mild detergent if needed). | Quarterly | Soft cloth, neutral cleaner | Avoid alcohol, acetone, or abrasive cleaners. |
| Bend Radius Verification | Ensure no sharp bends (maintain ≥8cm radius). | Post-installation + Annually | Tape measure | Kinks restrict flow and damage internal structure. |
| Environment Check | Confirm hose is >30cm from heat sources and shielded from UV rays. | Every 6 months | - | PVC degrades under high temps or sunlight. |
| Pressure Test | Professional verification of system pressure (≤0.1MPa). | Every 2 years | Pressure gauge | Overpressure risks PVC rupture. |
| Lifespan Tracking | Label installation date; replace every 3-5 years. | At installation | Marker pen | Internal metal corrosion may be invisible. |
Emergency Response
Gas Leak Detected:
Shut off valve immediately.
Ventilate area.
Avoid operating electrical devices.
PVC Melting/Damage:
Cut off gas supply.
Cool affected area with wet cloth (if safe).
Contact licensed technician for replacement.
Comparison with Metal Hoses
| Maintenance Aspect | PVC-Coated Hose | Stainless Steel Hose |
| Corrosion Focus | PVC layer integrity | Metal body rust/thread damage |
| Replacement Cycle | 3-5 years | 5-10 years |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Critical (≤60°C) | Tolerant (≤150°C) |
6. PVC Coated Gas Connector FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: What is a PVC-coated gas connector?
A1:
A PVC-coated gas connector is a flexible connecting pipe used to connect gas appliances (such as gas stoves, water heaters, gas boilers, etc.) to gas pipelines. Its core structure usually consists of a stainless steel corrugated pipe as the inner pressure-bearing layer, with an outer protective coating of PVC (polyvinyl chloride).
The main function of the PVC coating is to improve insulation, prevent oil and dirt buildup, prevent corrosion, extend the service life of the hose, and reduce the environmental impact of exposed metal.
Compared with ordinary hoses, PVC-coated gas connectors are more durable and safer.
Q2: What are the functions of the PVC coating?
A2:
The PVC coating is a key feature of this type of connector, and its main functions are as follows:
Corrosion resistance: Isolates moisture, oil, and acids and alkalis, preventing direct contact between stainless steel and the environment.
Scratch resistance: Prevents wear and tear on the metal outer wall, extending its lifespan.
Insulation protection: Effectively reduces the risk of static electricity accumulation and contact with external metal.
Extended service life: The overall lifespan is longer than that of uncoated metal hoses.
More aesthetically pleasing and easy to clean: The surface is smooth, and kitchen grease can be easily wiped off.
Q3: Are PVC-coated gas connectors safer than ordinary rubber hoses?
A3:
Overall, PVC-coated gas connectors are safer and more durable than rubber hoses. The reasons include:
The stainless steel inner layer can withstand higher pressure.
It is not prone to aging and will not be quickly damaged by high temperatures or oil.
It has a longer service life, generally 8–15 years (depending on the environment).
It is less susceptible to damage from biting, scratching, or compression.
It is more corrosion-resistant and temperature-resistant.
Therefore, it is the more recommended choice in modern homes and commercial kitchens.
Q4: How long can a PVC-coated gas connector be used?
A4:
Under normal use and correct installation, its service life is usually 8–15 years. Factors affecting lifespan include:
Exposure to continuous high temperatures
Subjecting it to strong bending or pulling
Contact with corrosive substances
Whether the installation method complies with specifications
It is recommended to inspect the hose every 1–2 years and replace worn or aged hoses promptly.
Q5: Can PVC coated gas connectors be bent freely?
A5:
Although the hose is flexible, it should not be excessively bent or kinked.
Avoid the following during use:
Sharp U-shaped bends
Sharp bends at small angles
Being bent or stretched for extended periods
The correct approach is to maintain a slight, natural curve. This prevents metal fatigue and localized damage to the outer PVC layer.
Q6: What should be noted when installing PVC coated gas connectors?
A6:
The main points to note are:
Avoid twisting during installation → Maintain consistent direction during installation; do not force twisting.
Do not exceed the maximum extension length → Some models are telescopic hoses; extending them to the maximum will affect their lifespan.
Do not place near high-temperature sources (such as the side wall of an oven) → High temperatures will cause the PVC coating to age.
Special fittings must be used for connections at both ends → Ensure airtightness.
Check for airtightness → After installation, use soapy water to check for leaks.
Q7: Can PVC coated gas connectors be used outdoors?
A7:
Yes, but under certain conditions:
Choose models with a UV-resistant (ultraviolet protection) coating
Keep away from areas prone to rain or moisture
Avoid direct sunlight and high-temperature exposure
Prevent damage from animal bites
For long-term outdoor use, it is recommended to choose metal-protected or reinforced PVC coated hoses.
Q8: If the PVC coating is damaged, does it need to be replaced immediately?
A8:
Yes, immediate replacement is recommended.
Even if the damaged area does not affect the inner metal pipe, it will lead to:
Exposure of the inner metal layer, accelerating corrosion
Reduced insulation protection
Easy accumulation of oil and dirt, causing external corrosion
For products involving gas safety, any damage requires replacement to avoid potential hazards.
Q9: What are the common failures of PVC coated gas connectors? A9:
Common malfunctions include:
Aging and cracking of the outer PVC layer
Deformation of the inner stainless steel pipe due to excessive bending
Loose connections causing gas leaks
Damage to the connector due to external force pulling on the hose
Softening or discoloration of the PVC due to proximity to high temperatures
Localized corrosion due to long-term exposure to oil and grease
If any of the above abnormalities are found, they should be dealt with or replaced promptly.
Q10: Can a PVC-coated gas connector be installed by myself?
A10:
To ensure safety, it is recommended that a professional install it.
If the user must install it themselves, they should:
Use appropriate tools
Install according to the instructions
Do not use Teflon tape to replace the special sealing ring
Perform a leak test after completion
Household gas is a high-risk item, and professional installation is more reliable.